What is Software Testing
Definition : The process or method of finding error/s in a software application or program so that the application functions according to the end user's requirement is called software testing.
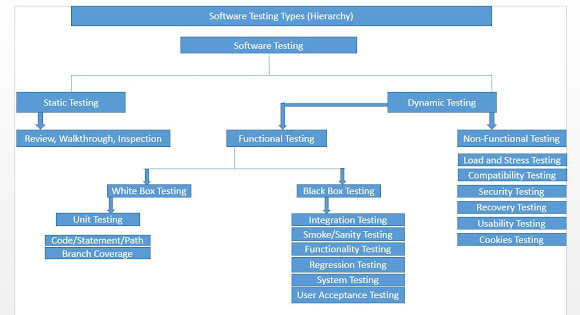
Types of Software Testing :
- Manual Testing
- Automation Testing.
Static Testing:
A type of testing carried
out without actually running the code. It involves activities like reviews,
inspections, and walk-throughs.
Static Testing Contain Following :
Review, Walkthrough, Inspection:
Walkthrough. An author presents the
work artifact to others. If the work artifact is code, the author walks through
the code, explaining what this pieces does, what that piece does. If the author
is like me, the author trails off in the middle of a sentence and says, “Oh no,
that's not what I wanted.” Or, “There's the problem.”
Inspection. An author requests the
services of a moderator, scribe, and reader/reviewers in a formal meeting. The
moderator books the room, sends out the material. The reader/reviewers read the
material before the meeting. During the meeting, the reader/reviewers take
turns reading the work artifact out loud. The scribe takes notes of issues the
reader/reviewers discovered in advance and during the meeting.
Review : A review is a
systematic examination of a document by one or more people with the main aim of
finding and removing errors early in the software development
life cycle. Reviews are used to verify documents such as requirements,
system designs, code, test plans and test cases.
Dynamic Testing:
It is performed by executing or running the application under test either manually or using automation. It is the opposite of the static testing which includes – reviews and walkthroughs.
Functional Testing:
Functional testing is
a quality assurance process and a type of black-box testing that bases its test
cases on the specifications of the software component under test. Functions are
tested by feeding them input and examining the output, and internal program
structure is rarely considered
Non –functional Testing:
Non-functional testing
is the testing of a software application or system for its non-functional
requirements: the way a system operates, rather than specific behaviours of that
system
Non Functional testing
solely focuses on the good quality of the software especially the non-functional aspects such as response time, security, scalability, usability, performance
etc. Non-functional software testing ensures that an application meets the
identified and specified performance requirements. Ultimately, it covers all
the tests that are not covered in the functional testing.
Comments
Post a Comment